Abstract

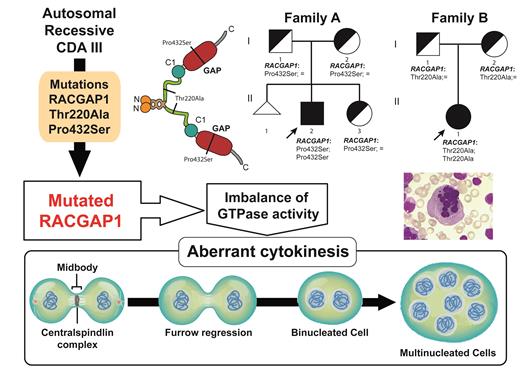
An autosomal dominant form of congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type III (CDA III) is caused by a missense mutation in the KIF23 gene whose protein product, mitotic kinesin-like protein (MKLP1), is part of the centralspindlin complex involved in cytokinesis. Several case reports suggested the existence of an autosomal recessive inheritance form of CDA III so far not genetically characterized. By means of whole exome sequencing in a Spanish CDA III family with healthy parents, we identified in the male proband a novel homozygous missense mutation p.Pro432Ser in the RACGAP1 gene, which encodes for the RACGAP1 protein (Rac GTPase-activating protein 1, also known as MgcRacGAP or CYK-4), the partner of MKLP1 in the centralspindlin complex. A second CDA III Spanish patient has a different rare and novel homozygous missense mutation, p.Thr220Ala, in the RACGAP1 gene. Both patients presented with macrocytic anemia, aberrant multinucleated erythroblasts in the bone marrow typically seen in CDA III cases, no iron overload and skull defects secondary to severe anemia. Silencing of RACGAP1 using siRNA in HeLa cells mimics the cytokinesis defect observed in the bone marrow of our patients. Both mutations disrupt normal cytokinesis and alter the GTPase balance in patients' cells. We conclude that the autosomal recessive form of CDA type III is caused by mutations in the RACGAP1 gene, encoding for RACGAP1 protein, which is the partner of MKLP1 in the centralspindlin complex critical for cytokinesis and now both proteins are associated with CDA type III.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal